E1 CRM Entity
E7 Activity
E11 Modification
E18 Physical Thing
E19 Physical Object
E22 Man-Made Object
E24 Physical Man-Made Thing
E25 Man-Made Feature
E26 Physical Feature
E33 Linguistic Object
E34 Inscription
E36 Visual Item
E37 Mark
E38 Image
E53 Place
E55 Type
E56 Language
E57 Material
E62 String
E70 Thing
E73 Information Object
P2 has type
P3 has note
P31 has modified
P32 used general technique
P45 consists of
P55 has current location
P56 bears feature
P59 has section
P65 shows visual item
P72 has language
P73 has translation
P128 carries
P130 shows features of


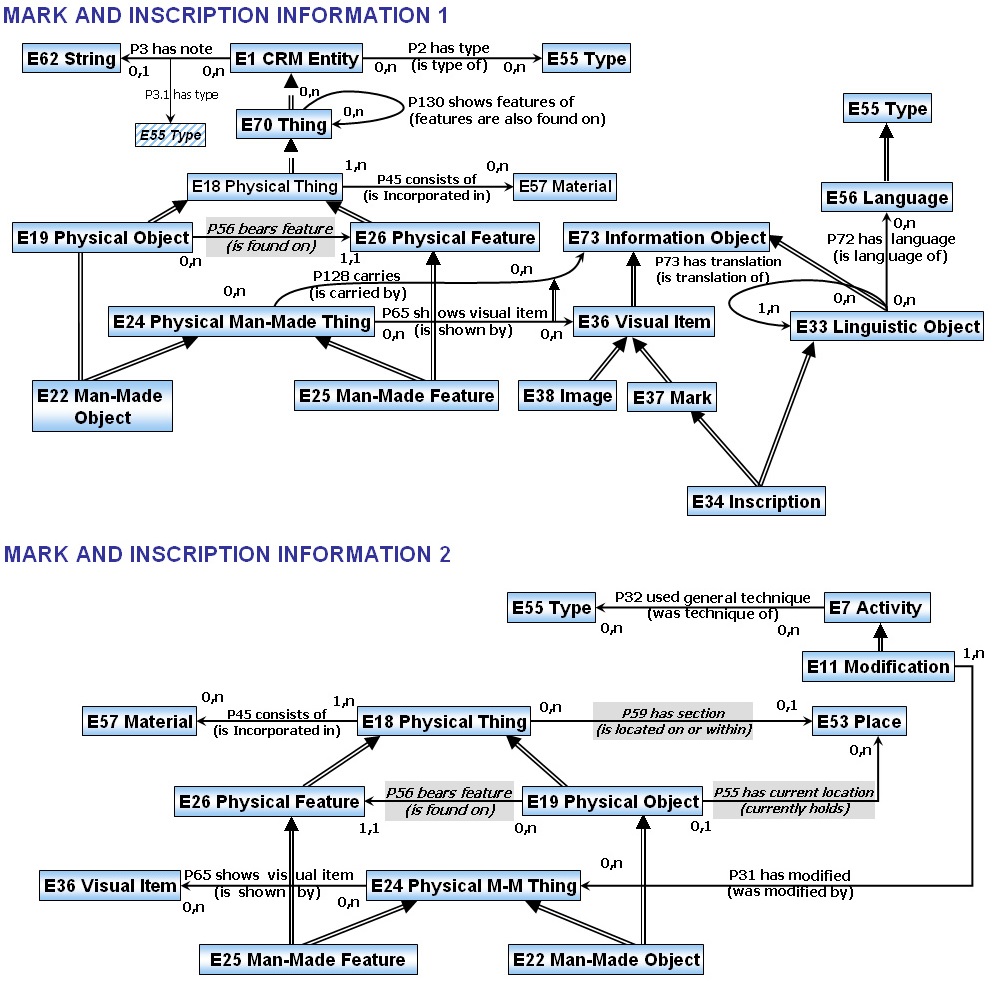
Motivation for these graphs has been the Mark and Inscription Information Group of the International Guidelines for Museum Object Information: The CIDOC Information Categories and other domain expert knowledge about marks and inscriptions, as well as interpretation of characteristic database schema elements from relevant collection management systems.
According to the International Guidelines for Museum Object Information: The CIDOC Information Categories, mark and inscription information supports Security, Accountability, Access, and an Historic archive. It enables the retrieval of lost property and the unique identification of otherwise similar objects and can be of particular research significance. In relation to marks and inscriptions the following information categories should be recorded:
In the CIDOC CRM the inscription is regarded on one side as a man-made feature (E25) which is found on a place (E53) located on the carrier object (E18). On the other side it is regarded as an immaterial visual item, which can be found on many carriers in the same form.